本地的镇江网站建设chrome浏览器下载安卓手机
什么是树
- 一种
分层数据的抽象模型。 - 前端工作中常见的树包括:DOM树,级联选择,树形控件
- JS中没有树,可以用Object和Array构建树
- 树的常用操作:
深度/广度优先遍历,先中后序遍历
深度优先遍历
- 访问
根节点 - 对根节点的
children挨个进行深度优先遍历
代码展示:
const tree = {val: 'a',children: [{val: 'b',children: [{val: 'd',children: []},{val: 'e',children: []}]},{val: 'c',children: [{val: 'f',children: []},{val: 'g',children: []}]}],
};const dfs = (root) => {console.log(root.val);root.children.forEach(dfs);
}dfs(tree);
输出顺序:a -> b -> d -> e -> c -> f -> g
广度优先遍历
- 新建一个
队列,把根节点入队 - 把
队头出队并访问 - 把
队头的children分别入队 - 重复二,三步,直到队列为空
代码展示:
const bfs = (root) => {const q = [root];while (q.length) {const n = q.shift();console.log(n.val);n.children.forEach((child) => {q.push(child);})}
}bfs(tree);
输出顺序:a -> b -> c -> d -> e -> f -> g
先序遍历
- 访问
根节点 - 对根节点的
左子树进行先序遍历 - 对根节点的
右子树进行先序遍历
代码展示:
const bt = {val: 1,left: {val: 2,left: {val: 4,left: null,right: null},right: {val: 5,left: null,right: null}},right: {val: 3,left: {val: 6,left: null,right: null},right: {val: 7,left: null,right: null}}
};
// 递归
const preorder = (root) => {if (!root) return;console.log(root.val);preorder(root.left);preorder(root.right);
}preorder(tree);// 迭代
const preorder = (root) => {if (root) return;const stack = [root];while (stack.length) {const n = stack.pop();console.log(top.val);if (n.right) stack.push(n.right);if (n.left) stack.push(n.left);}}
}preorder(tree);
参考视频:传送门
输出顺序:1 -> 2 -> 4 -> 5 -> 3 -> 6 -> 7
中序遍历
- 对根节点的
左子树进行中序遍历 - 访问
根节点 - 对根节点的
右子树进行中序遍历
代码展示:
// 递归
const inorder = (root) => {if (!root) return;preorder(root.left);console.log(root.val);preorder(root.right);
}inorder(tree);// 迭代
const inorder = (root) => {if (!root) return;const stack = [];let p = root;while (stack.length || p) {while (p) {stack.push(p);p = p.left;}const n = stack.pop();console.log(n.val);p = n.right;}
}inorder(tree);
输出顺序:4 -> 2 -> 5 -> 1 -> 6 -> 3 -> 7
后序遍历
- 对根节点的
左子树进行后序遍历 - 对根节点的
右子树进行后序遍历 - 访问
根节点
代码展示:
// 递归
const postorder = (root) => {if (!root) return;preorder(root.left);preorder(root.right);console.log(root.val);
}postorder(tree);// 迭代
const postorder = (root) => {if (!root) return;const stack = [root];const outputStack = [];while (stack.length) {const n = stack.pop();outputStack.push(n);if (n.left) stack.push(n.left);if (n.right) stack.push(n.right);}while (outputStack) {const n = outputStack.pop();console.log(n.val);}
}postorder(tree);
输出顺序:4 -> 5 -> 2 -> 6 -> 7 -> 3 -> 1
leetcode题目
难度:简单
- 二叉树的最大深度
思路:
- 求最大深度,优先考虑
深度优先遍历 - 在深度优先遍历过程中,
记录每个节点所在的层级,找到最大的层级即可
代码展示:
/*** @param {TreeNode} root* @return {number}*/
var maxDepth = function(root) {let maxDepth = 0;const dfs = (n, l) => {if (!n) return;dfs(n.left, l + 1);dfs(n.right, l + 1);if (!n.left && !n.right) maxDepth = Math.max(maxDepth, l);}dfs(root, 1);return maxDepth;
};
复杂度分析:
-
时间复杂度:O(n):n为二叉树节点个数。
-
空间复杂度:O(height):height为二叉树的最大深度。在平均情况下,二叉树的高度与节点个数为对数关系,即 O(logN)。而在最坏情况下,树形成链状,空间复杂度为 O(N)。
- 翻转二叉树
思路:
- 方法一使用
广度优先遍历,在遍历树的过程中,交换当前层级下的左右子树 - 方法二使用
递归解决,递归最重要的是定义子问题。
代码展示:
方法一:广度优先遍历
/*** @param {TreeNode} root* @return {TreeNode}*/
var invertTree = function(root) {if (!root) root;const bfs = (root) => {const q = [root];while (q.length) {const n = q.shift();const temp = n.right;n.right = n.left;n.left = temp;if (n.left) q.push(n.left);if (n.right) q.push(n.right);}}bfs(root);return root;
}
方法二:递归
/*** @param {TreeNode} root* @return {TreeNode}*/
var invertTree = function(root) {if (!root) return null;let newTree = new TreeNode(root.val);newTree.left = invertTree(root.right);newTree.right = invertTree(root.left);return newTree;
};
复杂度分析:
-
时间复杂度:O(n):n为二叉树节点个数。
-
空间复杂度:O(height):height为二叉树的最大深度。在平均情况下,二叉树的高度与节点个数为对数关系,即 O(logN)。而在最坏情况下,树形成链状,空间复杂度为 O(N)。
- 对称二叉树
思路:
- 通过遍历比较两个相同根节点的左子树和右子树的值是否相等
- 如果每次都相等,直到两个节点都不存在,说明是对称的
- 如果两个节点不相等,则说明不对称
代码展示:
/** * @param {TreeNode} root * @return {boolean} */
var isSymmetric = function(root) {if (!root) return false;const checkSym = (p, q) => {if (!p && !q) return true;if (!p || !q) return false;return p.val === q.val && checkSym(p.left, q.right) && checkSym(q.left, p.right);}return checkSym(root, root);
}
复杂度分析:
-
时间复杂度:O(n):n为二叉树节点数。
-
空间复杂度:O(n):n为二叉树节点数,最差情况为O(n)。
- 二叉树的直径
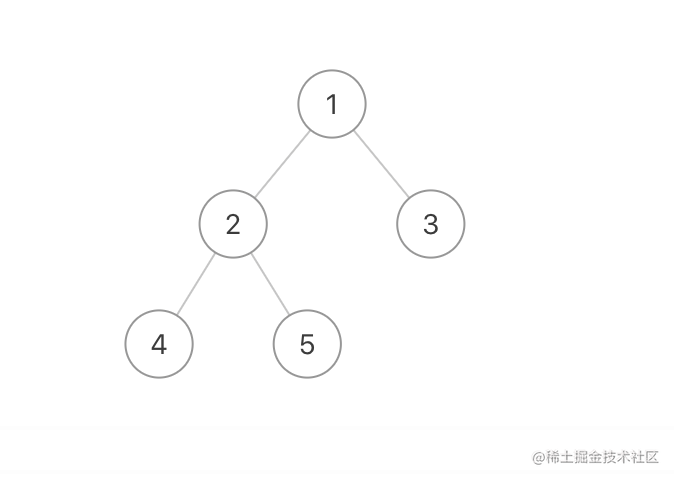
思路:
- 考虑
深度优先遍历 - 寻找两个最深的节点距离之和
代码展示:
/*** @param {TreeNode} root* @return {number}*/
var diameterOfBinaryTree = function(root) {if (!root) return 0;let res = 1; // 默认为根节点的路径长度const dfs = (root) => {if (!root) return 0;let L = dfs(root.left); // 左子树深度,上图为例,最长L为2let R = dfs(root.right); // 右子树深度,上图为例,最长R为1res = Math.max(res, L + R + 1); // 最大L+R+1,+1为根节点,总共深度为4,即节点树为4return Math.max(L, R) + 1; // 包含根节点的深度,上图为例,最长L为2,最长R为1}dfs(root);return res - 1; // 最终结果要得到直径为3
};
复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度:O(n):n为二叉树节点数。
- 空间复杂度:O(height):height为二叉树的最大深度。在平均情况下,二叉树的高度与节点个数为对数关系,即 O(logN)。而在最坏情况下,树形成链状,空间复杂度为 O(N)。
剑指 Offer 27. 二叉树的镜像
思路:
- 逐层递归互换左右子树节点的位置
代码展示:
/*** @param {TreeNode} root* @return {TreeNode}*/
var mirrorTree = function(root) {if (!root) return root;const temp = root.left;root.left = root.right;root.right = temp;mirrorTree(root.left);mirrorTree(root.right);return root;
}
优化后:
/** * @param {TreeNode} root * @return {TreeNode} */
var mirrorTree = function(root) {if (!root) return root;[root.left, root.right] = [mirrorTree(root.right), mirrorTree(root.left)];return root;
}
复杂度分析:
-
时间复杂度:O(n):n为二叉树节点数。
-
空间复杂度:O(n):n为二叉树节点树。
- 二叉树的最近公共祖先
剑指 Offer 68 - II. 二叉树的最近公共祖先
思路:
- 递归
代码展示:
/** * @param {TreeNode} root * @param {TreeNode} p * @param {TreeNode} q * @return {TreeNode} */
var lowestCommonAncestor = function(root, p, q) {// 当传入递归的树等于 p 或者等于 q,说明找到了 p 或者 q,返回给递归调用的 l 或 rif (!root || p === root || q === root) return root;let l = lowestCommonAncestor(root.left, p, q); // 递归调用,寻找 p 和 qlet r = lowestCommonAncestor(root.right, p, q); // 递归调用,寻找 p 和 qreturn l && r ? root : l || r; // 如果 p 和 q 分别在 root.left 和 root.right 中找到,则根节点 root 成为最近的公共祖先返回。// 假如 p 和 q 在 root.left 中找到,递归会把 p 和 q 的公共祖先返回给 l。// 假如,p 和 q 在 root.right 中找到,递归会把 p 和 q 的公共祖先返回给 r。// 根节点root,l 或 r 最终成为当前函数的返回值。
};
复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度:O(n):n为二叉树节点数。
- 空间复杂度:O(n):n为二叉树节点数。递归调用的栈深度取决于二叉树的高度,二叉树最坏情况下为一条链,此时高度为 N,因此空间复杂度为 O(N)。
剑指 Offer 55 - I. 二叉树的深度
思路:
- 考虑
深度优先遍历
代码展示:
var maxDepth = function (root) {if (!root) return 0;let max = 0;const dfs = (root, l) => {if (root.left) dfs(root.left, l + 1);if (root.right) dfs(root.right, l + 1);if (!root.left && !root.right) max = Math.max(max, l);}dfs(root, 1);return max;
}
复杂度分析:
-
时间复杂度:O(n):n为二叉树节点数,计算树的深度需要遍历所有节点。
-
空间复杂度:O(n):最差情况下,空间复杂度为O(n)。
- 二叉树的所有路径
思路:
- 本题考虑使用
深度优先遍历。 - 如果当前节点有
左子树或右子树,就递归调用函数,直到左右子树都不存在,此时就是我们要找的的路径。
代码展示:
/*** @param {TreeNode} root* @return {string[]}*/
var binaryTreePaths = function(root) {if (!root) return [];const res = [];const dfs = (root, path) => {if (root) {path += root.val;if (!root.left && !root.right) {res.push(path);} else {path += '->';dfs(root.left, path);dfs(root.right, path);}}}dfs(root, "");return res;
};
复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度:O(n^2):n为二叉树节点数。在深度优先搜索中每个节点会被访问一次且只会被访问一次,每一次会对 path 变量进行拷贝构造,时间代价为 O(N),故时间复杂度为 O(N^2)。
- 空间复杂度:O(n^2):n为二叉树节点数。
剑指 Offer 32 - I. 从上到下打印二叉树
剑指 Offer 32 - II. 从上到下打印二叉树 II
- 解题方法同二叉树的层序遍历
- 平衡二叉树
思路:
-
考虑
深度优先遍历 -
算出最大深度和最小深度的差值,即可判断是否为平衡二叉树 (本题和求二叉树直径做法类似)
代码展示:
/*** @param {TreeNode} root* @return {boolean}*/
var isBalanced = function(root) {if (!root) return true;let diff = 0;const dfs = (root) => {if (!root) return 0;let L = dfs(root.left);let R = dfs(root.right);diff = Math.max(diff, Math.abs(R - L));return Math.max(L, R) + 1;}dfs(root);return diff - 1 <= 0;
};
复杂度分析:
-
时间复杂度:O(n):n为二叉树节点数。
-
空间复杂度:O(n):n为二叉树节点数,最差情况为O(n)。
- 合并二叉树
思路:
- 递归对两个相同位置的节点相加
代码展示:
/*** @param {TreeNode} root1* @param {TreeNode} root2* @return {TreeNode}*/
var mergeTrees = function(root1, root2) {if (!root1 || !root2) return root1 || root2;let newRoot = new TreeNode(root1.val + root2.val);newRoot.left = mergeTrees(root1.left, root2.left);newRoot.right = mergeTrees(root1.right, root2.right);return newRoot;
};
复杂度分析:
-
时间复杂度:O(n):n为二叉树节点数。
-
空间复杂度:O(n):n为二叉树节点数。
- 路径总和
思路:
- 考虑
深度优先遍历 - 记录从根节点到当前节点的和,与target比较。
代码展示:
/** * @param {TreeNode} root * @param {number} targetSum * @return {boolean} */
var hasPathSum = function(root, targetSum) {if (!root) return false;let res = false;const dfs = (root, val) => {if (root.left) dfs(root.left, val + root.left.val);if (root.right) dfs(root.right, val + root.right.val);if (!root.left && !root.right && val === targetSum) res = true;}dfs(root, root.val);return res;
};
复杂度分析:
-
时间复杂度:O(n):n为二叉树节点数。
-
空间复杂度:O(n):n为二叉树节点数。
- 二叉树的最小深度
思路:
-
方法一考虑使用
广度优先遍历 -
方法二考虑使用
深度优先遍历
代码展示:
方法一:
/*** @param {TreeNode} root* @return {number}*/
var minDepth = function(root) {if (!root) return 0;let minDep = Infinity;const bfs = (root, l) => {const q = [[root, l]];while (q.length) {const [n, l] = q.shift();if (n.left) q.push([n.left, l + 1]);if (n.right) q.push([n.right, l + 1]);if (!n.left && !n.right) minDep = Math.min(minDep, l);}}bfs(root, 1);return minDep;
};
方法二:
/** * @param {TreeNode} root * @return {number} */
var minDepth = function(root) {if (!root) return 0;if (root.left && root.right) {return 1 + Math.min(minDepth(root.left), minDepth(root.right));} else if (root.left) {return 1 + minDepth(root.left);} else if (root.right) {return 1 + minDepth(root.right);} else {return 1;}
};
复杂度分析:
-
时间复杂度:O(n):n为二叉树节点数。
-
空间复杂度:O(n):n为二叉树节点数。
- N 叉树的前序遍历
思路:
- 类似于二叉树的前序遍历
代码展示:
// 递归
var preorder = function(root) {if (!root) return [];const res = [];const preord = (n) => {if (n) res.push(n.val);n.children.forEach(preord);}preord(root);return res;
};// 迭代
var preorder = function(root) {if (!root) return [];const stack = [root];const res = [];while (stack.length) {const n = stack.pop();res.push(n.val);n.children.reverse().forEach(child => {stack.push(child);});}return res;
}
复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度:O(n):n为二叉树节点数。
- 空间复杂度:O(height):height为二叉树最大深度。
剑指 Offer 54. 二叉搜索树的第k大节点
思路:
- 根据树的特点,采用
中序遍历,按右子树 - 根节点 - 左子树的顺序遍历,就可以由大到小找到第k大节点
代码展示:
/*** @param {TreeNode} root* @param {number} k* @return {number}*/
var kthLargest = function(root, k) {if (!root || k <= 0) return null;const stack = [];const res = null;let p = root;while (stack.length || p) {while (p) {stack.push(p);p = p.right;}const top = stack.pop();if (--k === 0) return top.val;p = top.left;}return res;
};
复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度:O(n):n为二叉树节点数。
- 空间复杂度:O(n):n为二叉树节点数。
难度:中等
- 二叉树的前序遍历
代码展示:
/*** @param {TreeNode} root* @return {number[]}*/
var preorderTraversal = function(root) {if (!root) return [];const stack = [root];const res = [];while (stack.length) {const n = stack.pop();res.push(n.val);if (n.right) stack.push(n.right);if (n.left) stack.push(n.left);}return res;
};
复杂度分析:
-
时间复杂度:O(n):n为二叉树节点数。
-
空间复杂度:O(n)
- 二叉树的中序遍历
代码展示:
/*** @param {TreeNode} root* @return {number[]}*/
var inorderTraversal = function(root) {if (!root) return [];const stack = [];const res = [];let p = root;while (stack.length || p) {while (p) {stack.push(p);p = p.left;}const n = stack.pop();res.push(n.val);p = n.right;}return res;
};
复杂度分析:
-
时间复杂度:O(n):n为二叉树节点数。
-
空间复杂度:O(n)
- 二叉树的后序遍历
代码展示:
/*** @param {TreeNode} root* @return {number[]}*/
var postorderTraversal = function(root) {if (!root) return [];const stack = [root];const outputStack = [];const res = [];while (stack.length) {const n = stack.pop();outputStack.push(n);if (n.left) stack.push(n.left);if (n.right) stack.push(n.right);}while (outputStack.length) {const n = outputStack.pop();res.push(n.val);}return res;
};
复杂度分析:
-
时间复杂度:O(n):n为二叉树节点数。
-
空间复杂度:O(n)
- 二叉树的层序遍历
代码展示:
方法一:深度优先遍历
/*** @param {TreeNode} root* @return {number[][]}*/
var levelOrder = function(root) {if (!root) return [];const res = [];const dfs = ([root, l]) => {if (!res[l]) {res[l] = [root.val];} else {res[l].push(root.val)}if (root.left) dfs([root.left, l + 1]);if (root.right) dfs([root.right, l + 1]);}dfs([root, 0]);return res;
};
方法二:广度优先遍历
/*** @param {TreeNode} root* @return {number[][]}*/
var levelOrder = function(root) {if (!root) return [];let res = [];const bfs = (root, l) => {const q = [[root, l]];while (q.length) {const [n, l] = q.shift();if (!res[l]) res[l] = [];res[l].push(n.val);if (n.left) q.push([n.left, l + 1]);if (n.right) q.push([n.right, l + 1]);}};bfs(root, 0);return res;
};
复杂度分析:
-
时间复杂度:O(n):n为二叉树节点数。
-
空间复杂度:O(n)
-
从前序与中序遍历序列构造二叉树
-
从中序与后序遍历序列构造二叉树
剑指 Offer 07. 重建二叉树
思路:
- 递归
代码展示:
参考:多种解法,逐渐优化
/*** @param {number[]} preorder* @param {number[]} inorder* @return {TreeNode}*/
var buildTree = function(preorder, inorder) {if (!preorder.length || !inorder.length) return null;const map = new Map();for (let i = 0; i < inorder.length; i++) {map.set(inorder[i], i);}const builder = (p_start, p_end, i_start, i_end) => {if (p_start > p_end) return null;let rootVal = preorder[p_start]; // 找到根节点let root = new TreeNode(rootVal); // 设置二叉树的根节点let mid = map.get(rootVal); // 找到根节点在inorder中的位置let leftNum = mid - i_start; // 左子树的个数root.left = builder(p_start + 1, p_start + leftNum, i_start, mid - 1);root.right = builder(p_start + leftNum + 1, p_end, mid + 1, i_end);return root;}return builder(0, preorder.length - 1, 0, inorder.length - 1);
};
复杂度分析:
-
时间复杂度:O(n):n为二叉树节点数。
-
空间复杂度:O(n)
- 二叉树的锯齿形层序遍历
思路:
- 同二叉树层序遍历
代码展示:
/*** @param {TreeNode} root* @return {number[][]}*/
var zigzagLevelOrder = function(root) {if (!root) return [];const res = [];const bfs = ([root, index]) => {if (!root) return;if (!res[index]) {res[index] = [root.val];} else {index % 2 === 0 ? res[index].push(root.val) : res[index].unshift(root.val);}if (root.left) bfs([root.left, index + 1]);if (root.right) bfs([root.right, index + 1]);}bfs([root, 0]);return res;
};
复杂度分析:
-
时间复杂度:O(n):n为二叉树节点数。
-
空间复杂度:O(n)
- 二叉树的右视图
思路:
-
方法一考虑
广度优先遍历,每层保留最后一个元素 -
方法二考虑使用类似
先序遍历,根 - 右 - 左的方式遍历,每层第一个出现的元素保留下来即可
代码展示:
方法一:广度优先遍历
/*** @param {TreeNode} root* @return {number[]}*/
var rightSideView = function(root) {if (!root) return [];const res = [];const bfs = (root, l) => {const q = [[root, l]]while (q.length) {const [n, l] = q.shift();res[l] = n.val;if (n.left) q.push([n.left, l + 1]);if (n.right) q.push([n.right, l + 1]);}}bfs(root, 0);return res;
};
方法二:
/*** @param {TreeNode} root* @return {number[]}*/
var rightSideView = function(root) {if (!root) return [];const res = [];const stack = [[root, 0]];while (stack.length) {const [n, l] = stack.pop();if (res[l] == undefined) res.push(n.val);if (n.left) stack.push([n.left, l + 1]);if (n.right) stack.push([n.right, l + 1]);}return res;
};
复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度:O(n):n为二叉树节点数。
- 空间复杂度:O(n)
剑指 Offer 26. 树的子结构
思路:
- 递归比较
代码展示:
/** * @param {TreeNode} A * @param {TreeNode} B * @return {boolean} */
var isSubStructure = function(A, B) {if (!A || !B) return false;const isSameSub = (p, q) => {if (!q) return true;if (!p) return false;if (p.val !== q.val) return false;return isSameSub(p.left, q.left) && isSameSub(p.right, q.right);}return isSameSub(A, B) || isSubStructure(A.left, B) || isSubStructure(A.right, B);
};
复杂度分析:
-
时间复杂度:O(mn):m,n分别为A和B的节点数。
-
空间复杂度:O(m)
- 验证二叉搜索树
代码展示:
/** * @param {TreeNode} root * @return {boolean} */
var isValidBST = function(root) {const helper = (root, lower, upper) => {if (root === null) {return true;}if (root.val <= lower || root.val >= upper) {return false;}return helper(root.left, lower, root.val) && helper(root.right, root.val, upper);}return helper(root, -Infinity, Infinity);
};
复杂度分析:
-
时间复杂度:O(n):n为二叉树节点数。
-
空间复杂度:O(n)
- 不同的二叉搜索树
思路:
- 卡塔兰数公式
代码展示:
var numTrees = function(n) {let C = 1;for (let i = 0; i < n; ++i) {C = C * 2 * (2 * i + 1) / (i + 2);}return C;
};
复杂度分析:
-
时间复杂度:O(n):n为二叉树节点数。
-
空间复杂度:O(1)
- 完全二叉树的节点个数
代码展示:
/** * @param {TreeNode} root * @return {number} */
var countNodes = function(root) {return root ? countNodes(root.left) + countNodes(root.right) + 1 : 0;
};
复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度:O(n):n为二叉树节点数。
- 空间复杂度:O(1)
剑指 Offer 34. 二叉树中和为某一值的路径
代码展示:
/*** @param {TreeNode} root* @param {number} target* @return {number[][]}*/
var pathSum = function(root, target) {if (!root) return [];const res = [];let temp = [];const dfs = (root, v) => {if (!root) return null;temp.push(root.val);if (root.left) dfs(root.left, root.left.val + v);if (root.right) dfs(root.right, root.right.val + v);if (!root.left && !root.right && v === target) {res.push([...temp]);}temp.pop();}dfs(root, root.val);return res;
};
复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度:O(n):n为二叉树节点数。
- 空间复杂度:O(n)
难度:困难
- 二叉树中的最大路径和
代码展示:
参考解法
/*** @param {TreeNode} root* @return {number}*/
var maxPathSum = function(root) {let maxNum = Number.MIN_SAFE_INTEGER;const dfs = (root) => {if (!root) return 0;const left = dfs(root.left);const right = dfs(root.right);const curMaxSum = left + root.val + right; // 当前子树内部最大路径和maxNum = Math.max(maxNum, curMaxSum);const outputMaxSum = root.val + Math.max(left, right); // 当前子树对上一层输出的最大路径和return outputMaxSum > 0 ? outputMaxSum : 0; // 大于0有输出的必要,小于0就返回0};dfs(root);return maxNum;
}
复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度:O(n):n为二叉树节点数。
- 空间复杂度:O(n)
剑指 Offer 37. 序列化二叉树
总结
继续对树的深度/广度优先遍历,先中后序遍历,层序遍历等遍历和递归的方法,有更深入的理解和学习。
