文件处理技术 System.IO命名空间 System.IO命名空间常用的类 System.IO命名空间常用的枚举 File类的常用方法 File类的常用静态方法 FileInfo类的常用方法 File类和FileInfo类的区别 文件夹类Directory的常用方法 文件流类FileStream
类 说明 File 提供用于创建,复制,删除,移动和打开文件的静态方法,并协助创建FileStream对象 FileInfo 提供用于创建,复制,删除,移动和打开文件的实例方法,并且帮助创建FileStream对象。无法继承此类 FileStream 公开以文件为主的Stream,即支持同步读写操作,也支持异步读写操作 BinaryReader 用特定的编码将基元数据类型读作二进制值 BinaryWriter 以二进制形式将基元类型写入流,并支持用特定的编码写入字符串 BufferedStream 给另一流上的读写操作添加一个缓冲层。无法继承此类 Directory 公开用于创建,移动和枚举目录和子目录的静态方法。无法继承此类 DirectoryInfo 公开用于创建,移动和枚举目录和子目录的实例方法。无法继承此类 Path 对包含文件或目录路径信息的String实例执行操作。这些操作是以跨平台的方式执行的 StreamReader 实现一个TextReader,使其以一种特定的编码从字节流中读取字符 StreamWriter 实现一个TextWriter,使其以一种特定的编码向字节流中写入字符 FileSysWatcher 侦听文件系统更改通知,并在目录或目录中的文件发生更改时引发事件
枚举 说明 FileMode 指定操作系统打开文件的方式 FileShare 包含用于控制其他FileStream对象对同一文件可以具有的访问类型的常数 FileAccess 定义用于控制对文件的读访问,写访问或读/写访问的常数
方法 说明 Move 将指定文件移到新位置,并提供指定新文件名的选项 Delete 删除指定的文件。如果指定的文件不存在,则不引发异常 Copy 已重载。将现有文件复制到新文件 CreateText 创建或打开一个文件用于写入UTF-8编码的文本 OpenText 打开现有UTF-8编码文本文件以进行读取 Open 已重载。打开指定路径上的FileStream
private void FileDemo ( )
{ string = @"c:\temp\MyTest.txt" ; if ( ! File. Exists ( path) ) { using ( StreamWriter sw = File. CreateText ( path) ) { sw. WriteLine ( "Hello" ) ; sw. WriteLine ( "And" ) ; sw. WriteLine ( "Welcome" ) ; } } using ( StreamReader sr = File. OpenText ( path) ) { string = "" ; while ( ( s = sr. ReadLine ( ) ) != null ) { Console. WriteLine ( s) ; } } try { string = path + "temp" ; File. Delete ( path2) ; File. Copy ( path, path2) ; Console. WriteLine ( "{0} was copied to {1}." , path, path2 ) ; File. Delete ( path2) ; Console. WriteLine ( "{0} was successfully deleted." , path2) ; } catch ( Exception ex) { Console. WriteLine ( "The process failed:{0}" , ex. ToString ( ) ) ; }
} 方法 说明 CreateText(string FilePath) 创建或打开一个文件,用于写入UTF-8编码文本内容 OpenText(string FilePath) 打开现有UTF-8编码文本文件以进行读取 Open(string FilePath, FileMode) 打开指定路径上的FileStream,具有读/写访问权限 Create(string FilePath) 在指定路径中创建文件 OpenRead(string FilePath) 打开现有文件以进行读取 AppendText(string FilePath) 创建一个StreamWriter,它将UTF-8编码文本追加到现有文件
using System ;
using System. Collections. Generic ;
using System. ComponentModel ;
using System. Data ;
using System. Drawing ;
using System. IO ;
using System. Linq ;
using System. Text ;
using System. Threading. Tasks ;
using System. Windows. Forms ; namespace FileProcess
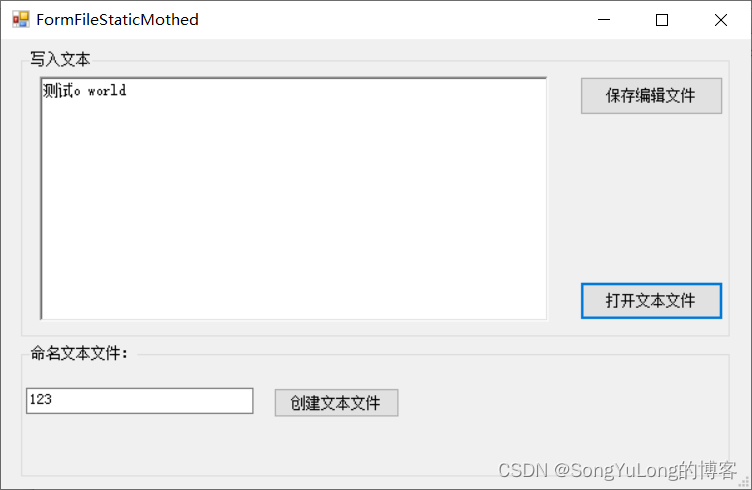
{ public partial class FormFileStaticMothed : Form { public FormFileStaticMothed ( ) { InitializeComponent ( ) ; } private static string = "C:\\temp\\" ; private void FormFileStaticMothed_Load ( object , EventArgs e) { } private void button1_Click ( object , EventArgs e) { try { if ( textBox1. Text. Length == 0 ) { MessageBox. Show ( "文件名禁止为空!" , "警报" ) ; } else { directory_path = directory_path + textBox1. Text. Trim ( ) + ".txt" ; StreamWriter sw = File. CreateText ( directory_path) ; button1. Enabled = false ; button2. Enabled = true ; button3. Enabled = true ; richTextBox1. Enabled = true ; MessageBox. Show ( "文件成功建立" , "消息" ) ; sw. Close ( ) ; } } catch ( Exception ex) { MessageBox. Show ( "磁盘操作错误,原因:" + Convert. ToString ( ex) , "警报" ) ; } } private void button3_Click ( object , EventArgs e) { try { OpenFileDialog open = new OpenFileDialog ( ) ; open. Title = "打开文本文件" ; open. FileName = "" ; open. AddExtension = true ; open. CheckFileExists = true ; open. CheckPathExists = true ; open. Filter = "文本文件(*.txt)|*.txt" ; open. ValidateNames = true ; if ( open. ShowDialog ( ) == DialogResult. OK) { Console. WriteLine ( open. FileName) ; StreamReader sr = new StreamReader ( open. FileName, System. Text. Encoding. Default) ; this . richTextBox1. Text = sr. ReadToEnd ( ) ; } MessageBox. Show ( "文件打开成功。" , "消息" ) ; } catch ( Exception ex) { MessageBox. Show ( "磁盘操作错误,原因:" + Convert. ToString ( ex) , "报警" ) ; } } private void button2_Click ( object , EventArgs e) { try { FileStream textFile = File. Open ( directory_path+ textBox1. Text. Trim ( ) + ".txt" , FileMode. OpenOrCreate, FileAccess. Write) ; StreamWriter sw = new StreamWriter ( textFile, Encoding. GetEncoding ( "GB2312" ) ) ; sw. Write ( richTextBox1. Text. ToString ( ) ) ; sw. Close ( ) ; MessageBox. Show ( "文件写成功。" , "报警" ) ; } catch ( Exception ex) { MessageBox. Show ( "磁盘操作错误,原因:" + Convert. ToString ( ex) , "报警" ) ; } } }
}
FileInfo提供创建,复制,删除,移动和打开文件的实例方法,并且帮助创建FileStream对象。
属性 说明 Attributes 获取或设置当前FileSystemInfo对象的FileAttributes属性(从FileSystemInfo类继承) CreationTime 获取或设置当前FileSystemInfo对象的创建时间(从FileSystemInfo类继承) Directory 获取父目录的实例 DirectoryName 获取表示目录的完成整路径的字符串 Exists 已重写。获取指示文件是否存在的值 Extension 获取表示文件扩展名部分的字符串(从FileSystemInfo类继承)
private void FileInfoDemo ( ) { string = "C:\\temp\\autoexec.bat" ; FileInfo fileInfo = new FileInfo ( fileName) ; if ( fileInfo. Exists) { return ; } Console. WriteLine ( "{0} has a directoryName of {1}" , fileName, fileInfo. DirectoryName) ; }
File和FileInfo综合示例
using System ;
using System. Collections. Generic ;
using System. ComponentModel ;
using System. Data ;
using System. Drawing ;
using System. Linq ;
using System. Text ;
using System. Threading. Tasks ;
using System. Windows. Forms ;
using System. IO ; namespace FileProcess
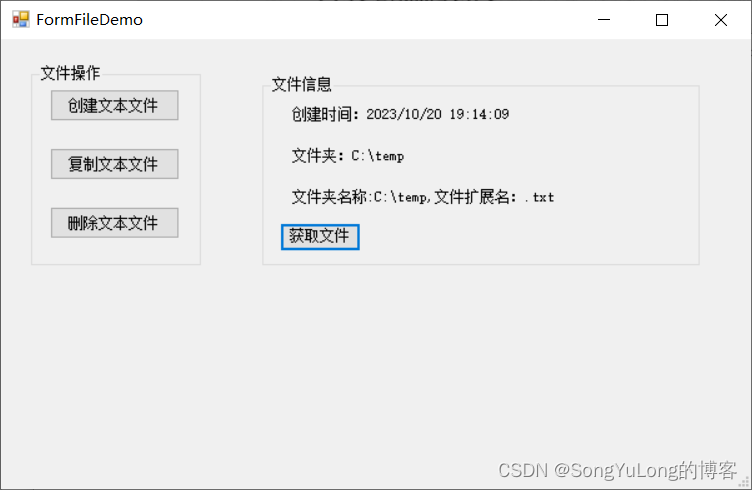
{ public partial class FormFileDemo : Form { public FormFileDemo ( ) { InitializeComponent ( ) ; } private void button1_Click ( object , EventArgs e) { string = @"C:\temp\1.txt" ; if ( File. Exists ( target) ) { File. Delete ( target) ; } File. CreateText ( target) ; MessageBox. Show ( "文件创建成功!" ) ; } private void button2_Click ( object , EventArgs e) { string = @"C:\temp\F1.txt" ; string = @"C:\temp\1.txt" ; if ( ! File. Exists ( someFile) ) { MessageBox. Show ( "文件不存在!" ) ; } else { if ( File. Exists ( target) ) { File. Delete ( target) ; } File. Copy ( someFile, target) ; MessageBox. Show ( "文件复制成功!" ) ; } } private void button3_Click ( object , EventArgs e) { string = @"C:\temp\1.txt" ; if ( File. Exists ( target) ) { File. Delete ( target) ; MessageBox. Show ( "文件删除成功!" ) ; } } private void button4_Click ( object , EventArgs e) { string = @"C:\temp\1.txt" ; FileInfo myFile = new FileInfo ( somefile) ; if ( myFile. Exists) { MessageBox. Show ( "文件已经存在" ) ; label1. Text = "创建时间:" + myFile. CreationTime. ToString ( ) ; label2. Text = "文件夹:" + myFile. Directory. ToString ( ) ; label3. Text = "文件夹名称:" + myFile. DirectoryName. ToString ( ) + ",文件扩展名:" + myFile. Extension. ToString ( ) ; } else { MessageBox. Show ( "文件不存在" ) ; } } }
}
File为静态类,可以直接使用;FileInfo需要实例化后才能使用。 从性能上考虑,如果要多次操作文件,不管是否针对相同文件,则应使用FileInfo。 每次通过File类调用某个方法时,都需要占用一定的CPU资源,而FileInfo类只在创建对象时执行一次安全检查。 Directory类公开用于创建,移动和枚举通过目录和子目录的静态方法。无法继承此类。
方法 说明 Move 蒋文件或目录及其内容移动到新位置 Delete 已重载。删除指定的目录 CreateDirectory 已重载。创建指定路径中的所有目录 GetCreationTime 获取目录的创建日期和时间 GetCurrentDirectory 获取引用程序的当前工作目录 GetFiles 已重载。返回指定目录中的文件的名称
using System ;
using System. Collections. Generic ;
using System. ComponentModel ;
using System. Data ;
using System. Drawing ;
using System. Linq ;
using System. Text ;
using System. Threading. Tasks ;
using System. Windows. Forms ;
using System. IO ; namespace FileProcess
{ public partial class FormDirectory : Form { public FormDirectory ( ) { InitializeComponent ( ) ; } private static string = "C:\\temp\\dir1" ; private static string = "C:\\temp\\dir2" ; private void DirectoryDemo ( ) { try { DateTime dt = Directory. GetCreationTime ( Environment. CurrentDirectory) ; if ( DateTime. Now. Subtract ( dt) . TotalDays > 364 ) { Console. WriteLine ( "This directory is over a year old." ) ; } else if ( DateTime. Now. Subtract ( dt) . TotalDays > 30 ) { Console. WriteLine ( "This directory is over a month old." ) ; } else if ( DateTime. Now. Subtract ( dt) . TotalDays <= 1 ) { Console. WriteLine ( "This directory is less than a day old." ) ; } else { Console. WriteLine ( "This directory was create on {0}" , dt) ; } } catch ( Exception ex) { Console. WriteLine ( "The process failed:{0}" , ex. ToString ( ) ) ; } } private void button1_Click ( object , EventArgs e) { DirectoryDemo ( ) ; } private void button2_Click ( object , EventArgs e) { try { Directory. CreateDirectory ( directory_path) ; button2. Enabled = false ; button3. Enabled = true ; button4. Enabled = true ; button5. Enabled = true ; button6. Enabled = true ; } catch ( Exception ex) { MessageBox. Show ( "磁盘操作错误,原因:" + Convert. ToString ( ex) , "警报" ) ; } } private void button3_Click ( object , EventArgs e) { try { Directory. Delete ( directory_path) ; button2. Enabled = true ; button3. Enabled = false ; button4. Enabled = false ; button5. Enabled = false ; button6. Enabled = false ; MessageBox. Show ( "文件夹已删除" , "警报" ) ; } catch ( Exception ex) { MessageBox. Show ( "磁盘炒作错误,原因:" + Convert. ToString ( ex) , "警报" ) ; } } private void button4_Click ( object , EventArgs e) { try { Directory. Move ( directory_path, directory_otherpath) ; MessageBox. Show ( "文件夹移动成功" , "警报" ) ; } catch ( Exception ex) { MessageBox. Show ( "磁盘操作错误,原因:" + Convert. ToString ( ex) , "警报" ) ; } } private void button5_Click ( object , EventArgs e) { try { MessageBox. Show ( string . Format ( "{0}:G" , Directory. GetCreationTime ( directory_path) ) , "提示" ) ; } catch ( Exception ex) { MessageBox. Show ( "磁盘操作错误,原因:" + Convert. ToString ( ex) , "报警" ) ; } } private void button6_Click ( object , EventArgs e) { try { string [ ] = Directory. GetFiles ( directory_path) ; if ( fileEntries. Length != 0 ) { foreach ( string in fileEntries) { if ( File. Exists ( s) ) { MessageBox. Show ( "内有文件信息:" + s, "提示" ) ; } } } else { MessageBox. Show ( "空文件夹" , "提示" ) ; } } catch ( Exception ex) { MessageBox. Show ( "磁盘操作错误,原因:" + Convert. ToString ( ex) , "报警" ) ; } } }
} FileStream文件流类简介要访问的文件。 表示如何打开文件的模式。 表示访问文件的方式:只读、只写、读写。 共享访问:表示是否独占访问文件。 FileStream文件流类的创建 : 使用File对象的Create方法。 使用File对象的Open方法。 使用类FileStream的构造函数。 FileStream类的3种常用构造函数
名称 说明 FileStream(string FilePath, FileMode) 使用指定的路径和创建模式初始化FileStream类的新实例 FileStream(string FilePath, FileMode, FileAccess) 使用指定路径,创建模式和读/写 权限初始化FileStream类的新实例 FileStream(string FilePath, FileMode, FileAccess, FileShare) 使用指定路径,创建模式,读/写权限和共享权限创建FileStream类的新实例
枚举类型FileMode,FileAccess和FileShare
名称 取值 说明 FileMode Append,Create,CreateNew,Open,OpenOrCreate和Truncate 指定操作系统打开文件的方式 FileAccess Read,Write和ReadWrite 定义访问权限 FileShare Inheritable,None,Read,ReadWrite和Write 包含用于控制其他FileStream对象对同一文件可以具有的访问类型的常数
枚举类型FileMode枚举值含义
Append 追加方式打开现有文件,或创建新文件。FileMode.Append只能同FileMode.Write一起使用。 Create 指定操作系统应创建新文件。如果文件已存在则被清空。如果文件不存在这用CreateNew;否则使用Truncate CreateNew 指定操作系统应创建新文件。此操作需要FileIOPermissionAccess.Write。如果文件已存在,则将引发IOException Open 指定操作系统打开心有文件。访问权限取决于FileAccess指定,文件不存在,则引发System.IO.FileNotFoundException Truncate 指定操作系统应打开现有文件。文件一旦打开,就会清空文件内容。
枚举类型FileAccess枚举值的含义
成员名称 说明 Read 对文件的读访问。 ReadWrite 对文件的读写访问。 Write 对文件的写访问。
枚举类型FileShare枚举值的含义
Delete 允许随后删除文件 Inheritable 使文件句柄可由子进程继承。Win32不直接支持此功能 None 谢绝共享当前文件。文件关闭前,打开该文件的任何请求都将失败 Read 允许随后打开文件读取。 ReadWrite 允许随后打开文件读写 Write 允许随后打开文件写入。